Copyright © Shanghai Omega Machinery Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Great Features and Benefits of Bimetallic Barrel
Mar 16,2017
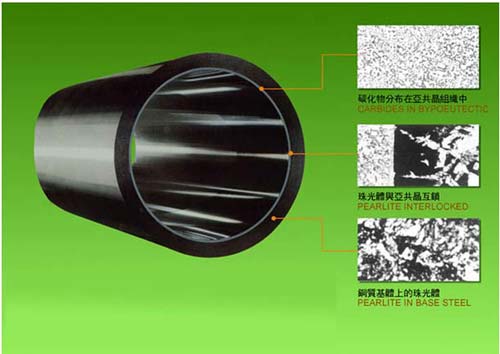
In today’s processing, the bimetallic barrels are widely used in the processing of modern plastics. In the plastification process, it requires the modern machine to create the most out of wear resistant system along with fibers and fillers. During the manufacturing process, the bimetallic barrel begins with a steel tube that is highly filled with the powdered metal and sealed the both ends.
After that, you just heated in a furnace at high temperature, which melts the powdered metal and then evenly distributed by centrifuging. Once you complete this process, you just cool the barrel under the specific controlled conditions and then get ready for upcoming processing. Here, the bimetallic is a protective layer and the barrel has been developed via a high quality control.
Moreover, the construction of bimetallic barrel offers a protective surface to the major strength of backing materials. The advantages of bimetallic barrel construction are providing the optimum process performance as well as increased the wear life. The main characteristics of bimetallic barrel can allow the process for continuous detection such as precise control, condition changes, similarity of barrel zone temperatures and the immediate response to heat as well as cool commands. This barrel construction process also reduces the wear gap and extends the productivity life as well. This bimetallic barrel has included the following features and benefits that include:
Features:
1. High performance backing material
2. Effective engineered design
3. Inseparable inlay bond
4. Bimetal construction
5. Extraordinary corrosion resistance
6. Wear and abrasion resistance on harsh layer
7. Hardness layer reaches around 1.5mm thickness
8. Outstanding wear or corrosion resistance
9. Toughness does not decrease with depth or under normal temperature
10. Bimetallic bore inlay
Benefits:
1. Maximize the process control
2. Efficient energy transfer
3. Increased barrel and screw life
4. Strengthen the resistance to fatigue
5. Optimum process performance
- Information
- What are the reasons for the bending and deformation of extruded plates? How can they be solved?
- What are the causes and solutions for uneven edges when extruding sheet materials?
- How to solve the problem of stripes appearing on the surface when producing ABS composite boards?
- What causes the appearance of pits and bubbles on the surface of ABS/PMMA co-extruded composite sheets? How can it be solved?
- Why does overflow occur at the exhaust port of the extrusion main machine when producing ABS multi-layer composite plates? How should it be handled?
- What are the differences in the process when producing UPVC pipes by directly extruding PVC granules and powder?
- How should one select the molding equipment when generating PP water supply pipes?
- Why do the surfaces of extruded profiles have weld marks when extruding? What are the solutions to eliminate these marks?
- Why do large, dull and unreflective bubbles appear on the surface of the special profiles? How can this problem be solved?
- What causes the uneven surface and poor gloss of the sheet during the sheet extrusion process? How can it be solved?
- Contact Us

-
Shanghai Omega Machinery Co., Ltd.
Add.: No.168 Hualian Road, Putuo District, Shanghai City
Contact: Nina
Tel.: +86-021-69921527
Mobile: +86-15021464410
Fax: +86-021-69921567
E-mail: omegajessica@163.com;965425705@qq.com
WeChat No.: 1131449532
Whatsapp: +86 159 0054 6558

-